The two largest blockchain platforms – Ethereum and Solana – are now in a fierce confrontation. Will the technological reform and transition to Ethereum 2.0 help Ether? Or has the originally more advanced Solana network escalated its growth momentum enough to overtake ETH?
What blockchain platform will become the new leader in the DeFi segment? Not that long ago, even asking the question was considered unwarranted, as few doubted the continuation of Ethereum’s reign. However, much more high-tech, fast, and scalable new platforms have since arrived to claim their share of the pie. And in the context of Ethereum’s sharply increased commissions, many crypto projects began flowing over to alternative blockchains and making good use of what those have to offer.
At this point, ETH’s main rival seems to be the Solana network. Here are a couple of infographics that display the current state of affairs:
This image is a year old now, but it clearly demonstrates that the Solana ecosystem is no longer inferior to the Ethereum one in richness and diversity.
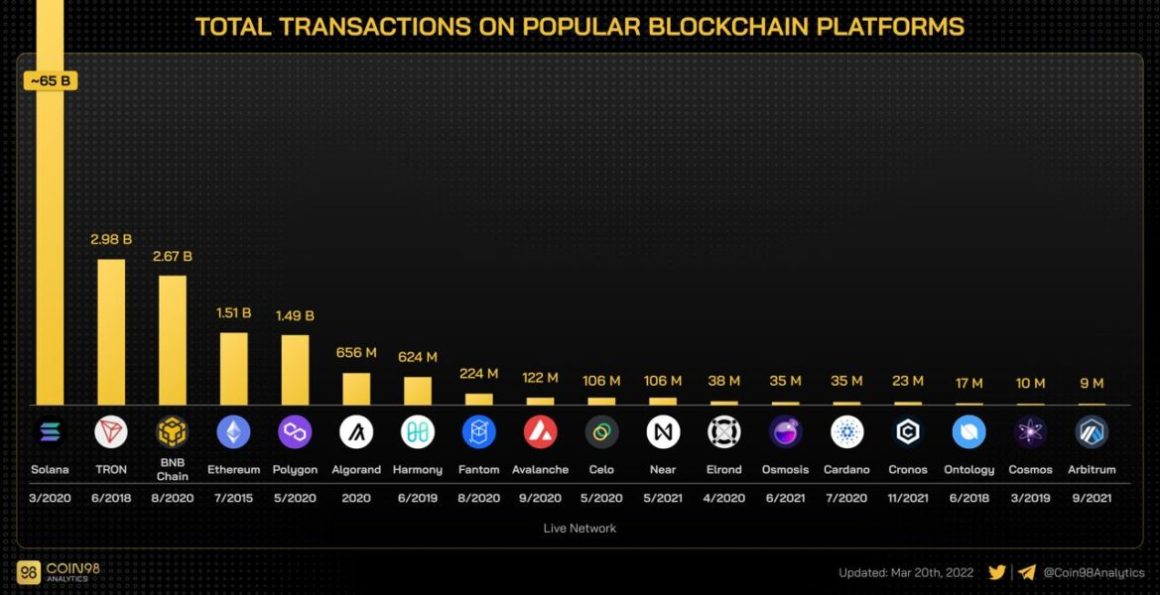
The second, more recent graph shows just how far Solana is ahead of all competitors in terms of on-chain transaction volume.
The Solana blockchain was, in fact, launched as “the Ethereum killer”. It gained popularity as a revolutionary in the field that filled in the gaps found in Ethereum. Solana can process around 60K transactions per second, making it one of the fastest Tier 1 blockchains. Although it is still under development, it has proven much more efficient, less expensive, and highly scalable.
Ethereum, on the other hand, is the flagship altcoin and the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization. Their decentralized blockchain is backed by the exceptionally proficient Ethereum Foundation and supports multi-chain networks, which significantly boosts scalability without sacrificing security.
Ethereum also has a larger NFT market compared to Solana. Despite recent advances in technology, Solana continues to lag far behind Ether’s NFT trading volumes.
In contrast with Ethereum’s consensus model, the Solana blockchain uses Proof of History to verify transactions. Major financial institutions such as JPMorgan and Bank of America have expressed confidence in Solana’s success; going as far as to state it could become “the backbone of the digital asset ecosystem”. Solana is also backed by the leading venture capital firm in the blockchain industry – Andreessen Horowitz.
Ethereum, on the other hand, has a very loyal user base, and a lot of veteran crypto users will likely stick with them for the foreseeable future. However, Solana operates at lightning speed, with commissions at a fraction of a percent. Since launching in 2020, it has come a long way to mass adoption by concluding over 60 billion transactions.
Quite aptly, in February of this year, the investment bank Morgan Stanley released a report called “What is Ethereum?” where they described in detail the ecosystem of the second-largest cryptocurrency. “Due in part to its more ambitious addressable market, Ethereum faces more competitive threats, scalability issues, and complexity challenges than Bitcoin. Furthermore, Ether is more volatile than Bitcoin,” the paper says.
According to bank analysts, Ethereum, as a platform for smart contracts, has more competitors than bitcoin, used primarily as a store of value. The experts point out that bitcoin often serves as a “decentralized savings account”, thus requiring fewer transactions. As such, the increase in network transaction price harms the demand for Ether more than for Bitcoin.
An additional problem is the greater centralization of Ethereum compared to bitcoin. The 100 largest addresses together own 14% of the first cryptocurrency, while for Ethereum the figure is 39%.
That being said, Morgan Stanley analysts still believe that the market potential of Ethereum is greater than that of Bitcoin. It also has a more pronounced deflationary component due to the burning mechanism built into transactions, while the intended transition to the PoS algorithm is supposed to make network operations much more efficient.
There is a psychological component to consider as well: many Ethereum supporters, in their criticism of Solana, find themselves in the position of the bitcoin community in its debate against digital asset skeptics. As is typical for many ideologies, they rationalize – adopt useful arguments against competitors but reject them if they contradict their own position.
In addition to Ethereum and Solana, there are five more projects that all boast high transaction speed, low fees, and positive long-term prospects – Fantom, Avalanche, Elrond, Tron, and Tezos.
The Fantom project has existed since 2018. This platform works on the Lachesis protocol, which is based on a combination of the PoS and aBFT consensus algorithms. The Fantom Opera network is compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and can be integrated with the Cosmos SDK. Their blockchain can be incorporated into other blockchains as a consensus module.
Fantom can perform up to 300,000 transactions per second. The DeFi architect of the project is one of the most iconic characters in the crypto community – Andre Cronje.
Avalanche is a smart contract platform. It has been around since 2018, but the official launch happened only in September 2020. Using the Avalanche functionality, developers can create public and private blockchains and select the desired programming language and the virtual machines (including EVM) for a particular blockchain to interact with.
The speed of the Avalanche blockchain is provided by the Snow protocol, which keeps the transaction time under two seconds. Another essential advantage of the protocol is its security. Avalanche can currently process up to 4500 transactions per second, and project representatives promise to bring this level to 20,000+ by applying second-level solutions.
Elrond is another smart contract platform, mainly meant for creating secure, high-performance DApps. The increased throughput of the Elrond network is achieved through a special sharding method called Adaptive State Sharding, in which the shard load is kept below 50%. The platform employs the Secure Proof of Stake (SPoS) consensus algorithm with a randomly selected block validator. The declared speed of Elrond testnet transactions is 250,000 per second, although the current network throughput is 15,000 transactions.
The Tron project launched its blockchain in 2018, becoming one of the first alternatives for Ethereum. Tron’s architecture is similar to Ether, but due to the use of the consensus algorithm, it is several times faster and has almost zero commissions. On the downside, Tron is substantially less decentralized.
Finally, the Tezos blockchain platform had a successful ICO but found itself in a difficult situation following a corporate conflict between the Breitman spouses – the project co-founders – and the head of the Tezos Foundation, Johann Gevers. As a result, the main network had only been launched by the fall of 2018.
Tezos uses the Liquid Proof of Stake consensus algorithm. New blocks are created through staking; the owners of the nodes in the Tezos network are called bakers. The platform has partners among major European financial institutions, including Crypto Finance AG and the Bank of France, which uses Tezos to create its digital currency.
So even if suddenly Ethereum and Solana fail to meet the expectations of new generations of DeFi service developers, there are alternatives for them to try out.



