On Dec. 30, 2023, Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin shared the Ethereum roadmap for 2024, pointing out that there are only a handful of minor adjustments compared to last year.
In a thread on the X social network, Buterin detailed in a series of charts and diagrams revealing that the continued focus for Ethereum in 2024 is on six main components – the Merge, the Surge, the Scourge, the Verge, the Purge and the Splurge.
By popular demand, an updated roadmap diagram for 2023! pic.twitter.com/oxo58A2KuG
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) December 30, 2023
The Merge was highlighted as a key section on the roadmap, aiming to maintain a simple and resilient proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus. It took place in September 2022 integrating the Ethereum mainnet with the PoS blockchain the Beacon Chain.
The Surge targets 100,000 transactions per second across Ethereum and layer 2 networks and aims to enhance the blockchain’s scalability.
The Scourge focuses on mitigating risks related to Maximal extractable value (MEV) and liquid pooling, addressing concerns about economic centralization within the Ethereum ecosystem.
Buterin also endorsed single-slot finality (SSF) as a crucial solution for Ethereum’s current weaknesses and praised advancements in layer 2 networks and Verkle tree implementations. Finality aims to ensure that changes to a blockchain block are irreversible without burning at least 33% of the total staked Ether.
The role of single slot finality (SSF) in post-Merge PoS improvement is solidifying. It's becoming clear that SSF is the easiest path to resolving a lot of the Ethereum PoS design's current weaknesses.
See:https://t.co/l8OcVsXCOWhttps://t.co/8sM6DieMjg pic.twitter.com/i6Gz36huW4
— vitalik.eth (@VitalikButerin) December 30, 2023
The Purge seeks to make the protocol easy to use, and the Verge aims to facilitate easier block verification while the Splurge encompasses all other elements crucial for Ethereum’s growth.
Ethereum improvement proposals (EIPs) to look out for
Earlier on Oct. 21, 2023, the Ethereum All Core Developers meeting provided some tentative dates on the upgrade schedule for the next mainnet hard fork, Dencun.
This was revealed in a series of posts on X by Ethereum Developer Tim Beiko who revealed that “if no major issues arise”, the forking of Ethereum’s public testnets is scheduled for Jan. 17 for Goerly, Jan. 30 for Sepolia and Jan. Feb. 7 for Holesky.
We'll also try and fork both networks within one week of each other, and have client releases which activate the upgrade on both testnets. This will save us one release cycle assuming nothing goes wrong.
— timbeiko.eth (@TimBeiko) December 21, 2023
This will be the last time that Goerli is included in the testing regimen, as the network is slated for deprecation, meaning client developers will no longer maintain it.
This move is part of the strategy to activate ‘Dencun’ on the Ethereum network in January 2024, marking a significant advancement in its technological capabilities.
Dencun is particularly expected to increase data availability for layer 2 rollups through EIP-4844 – Proto-Danksharding – resulting in a reduction of rollup transaction costs, which will be passed on to end-users.
Also key among the improvements on the Ethereum network are account abstraction: ERC-4337 and its extension, ERC-6900. It centers on the concept of smart accounts, which holds significant implications for end-user experience and will enable reduced transaction costs and secure social logins.
🦄 The top upcoming #Ethereum improvements for 2024:
1. EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding): This major proposal aims to reduce data availability costs across all layer-2 solutions, potentially slashing rollups gas fees by up to 100x.
2. ERC-4337 (Account Abstraction): This standard,…
— ∆mir/acc (@hey1994amir) January 2, 2024
EIP-1153 (Transient Storage Opcodes) and EIP-6780 (Restrict Self Destruct) are expected to reduce gas costs and enhance the network’s scalability and stability.
Upcoming Dencun upgrade could make Ethereum more competitive
There are narratives that Ethereum’s rivals are gaining relevance as critics argue that the ecosystem has failed due to its limited capacity for scaling and privacy solutions at the base layer level.
These negative conversations have been backed by the recent performance by Solana, Injective (INJ) and Avalanche which have gained 863%, 2,820% and 270%, respectively, over the last year against Ether’s 94%, according to data from CoinMarketCap.
I dont normally talk Dominance, but if I do it is $SOLD, $SOL dominance is very dominant considering this stage of the bull market. I shudder to think how high it could go – tomorrow will share math for a $5T CMC MC. pic.twitter.com/r4OyyzJjml
— InvestAnswers (@invest_answers) December 15, 2023
One of the key metrics determining the efficiency of a blockchain network depends on how affordable it is for users to process transactions. Transaction fees take into account the amount of computing power needed to process a transaction, known as gas, which also has a variable price measured in the native currency of the protocol and is directly related to network traffic.
According to a January 2023 report by BitfinityNetwork, the average cost per transaction on the Ethereum network is 33.5 Gwei, which is higher than the 5 Gwei for the BNB Chain.
Other blockchains such as Algorand (ALGO) and the Internet Computer (ICP) offer a negligible fixed fee that depends on the value of their token (0.001 ALGO and 0.0001 ICP, respectively), while using Polkadot costs nothing.
However, when it comes to Ethereum layer 2 solutions, the Ethereum network is unmatched with respect to DApps’ engagement backed by the dominance of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
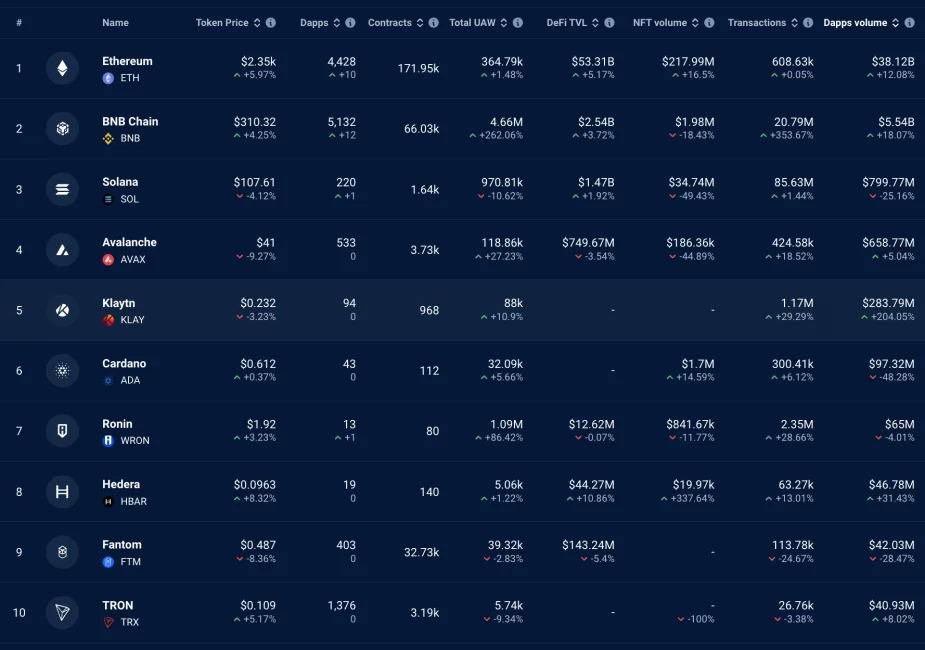
Data from DAppRaddar ranks Ethereum highest in terms of DApp volumes ahead of BNB Chain, Solana and Avalanche.
Apart from its absolute layer 1 dominance, the Ethereum network has posted a 16% growth in NFT volumes over the past 7 days, distancing itself from BNB Chain and Solana which are negative.
Moreover, the Ethereum network’s total value locked (TVL) of $53.32 billion invalidates much of the negative assessment. In comparison, BNB Chain holds a mere $2.54 billion TVL, while Solana’s latest data stands at $1.47 billion, according to DappRadar.
With the Dencun upgrade expected to make a significant reduction in transaction costs, Ethereum is slated to become even more competitive asserting its dominance over its rivals.
Source: https://cointelegraph.com/news/key-elements-to-watch-on-ethereum-network-roadmap